-
Products
- Lab Instruments
-
Lab Meters and Probes
Calibration Standards Other Meters and Probes
- Chemistries, Reagents, and Standards
-
Online Analyzers
Ammonium Analysers Chlorine Analyzers
- CL17sc
- CL10sc Amperometric
- 9184 sc Amperometric
- Ultra Low Range CL17sc Colorimetric Chlorine Analyser
EZ Series Analysers- Iron
- Aluminium
- Manganese
- Phosphate
- Chloride
- Cyanide
- Fluoride
- Sulphate
- Sulphide
- Arsenic
- Chromium
- Copper
- Nickel
- Zinc
- Ammonium
- Total Nitrogen
- Total Phosphorus
- Phenol
- Volatile Fatty Acids
- Alkalinity
- ATP
- Hardness
- Toxicity
- Sample Preconditioning
- Boron
- Colour
- Nitrate
- Nitrite
- Silica
- Hydrogen Peroxide
- EZ Series Reagents
- EZ Series Accessories
- EZ sc Series Inorganics
- EZ sc Series Metals
- EZ sc Series Nutrients
-
Online Sensors and Controllers
Digital Controllers (Transmitters) Controllers (Analog)
- SC4500
- Orbisphere 410/510 Carbon Dioxide
- Orbisphere 410/510 Oxygen
- Orbisphere 410/510 Ozone
- Pro Series
pH & ORP Sensors- 1200-S pH
- 12mm pH/ORP
- 8362 sc High Purity
- Combination pH/ORP
- Differential pH
- Digital Differential ORP
- Digital Differential pH
- LCP ORP
- LCP pH
Dissolved Oxygen Sensors- 2582sc
- 5500 Clark DO
- 9582 sc
- LDO 2 sc
- Orbisphere 311xx
- Orbisphere GA2x00
- Orbisphere K1X00
- Orbisphere M1100
- Orbisphere Oxygen ppb
Conductivity Sensors- 3400 Analogue Contacting
- 3400 Digital Contacting
- 3700 Analogue Inductive
- 3700 Digital Inductive
- 3798 sc Electrodeless
- 9523 Cation Conductivity
- 9525 DCCP System
- Samplers
- Multiparameter Online Panels
- Test Kits & Strips
-
Microbiology
Accessories and Chemicals Dehydrated MediaInstruments KitsLabware
- Automated Lab Systems
-
Lab Equipment and Supply
Apparatus
- Brushes
- Clamps, Rings & Stands
- Crucibles
- Crucibles & Casseroles
- Dispensers & Droppers
- Grab Samplers
- Oil and Grease
- Other Apparatus
- Pipet Aids
- Pipettes
- Racks
- Stir Bars
- Tubing
- Weighing Accessories
General Lab Consumables Glassware/PlasticwareInstruments- Balances
- Hot Plates & Stirrers
- Microscopes
- Moisture Analysers
- Other Instruments
- Ovens & Incubators
- Thermometers
- Timers
- Vacuum Pump
- Industrial UV
- Flow and Collections
- Electrochemistry
- Parameters
- Industries
- Support
- Service
- e-Shop
Hach India
Choose your country or region:
Europe
Americas
Asia - Australasia
- Australia
- Mainland China
- India
- Indonesia
- Japan
- Malaysia
- New Zealand
- Philippines
- Singapore
- South Korea
- Thailand (Thai)
- Taiwan
- Vietnam
Middle East - Africa
Promotions INQUIRY: +91 9916040249
Alkalinity
Understanding Alkalinity in Water
Alkalinity measures the capacity of water to neutralize acids and maintain a stable pH level. It is an important water quality indicator across a variety of applications including drinking water , beverages, boiler/cooling water and wastewater treatment
High alkalinity water can:
- Mitigate heavy metal's toxicity by using available bicarbonates and carbonates to remove metals from solutions.
- Create an objectionable carbonated taste in drinking water and can be harmful to human health
- Cause scaling or mineral build-up in industrial equipment and pipes
Low alkalinity water can:
- Make streams, rivers or lakes vulnerable to acidic pollutants which can drop the pH(link) of water to levels harmful for amphibians, fish or zooplankton
- Hinder the nitrification (links) process in biological wastewater treatment
Due to alkalinity's wide-ranging impacts, consistently monitor alkalinity is vital to maintaining healthy and stable water. Hach ® offers a wide range of testing equipment, resources, and software you need to successfully monitor alkalinity in your specific process application.
Featured Alkalinity Products
EZ Series Alkalinity Analyzers
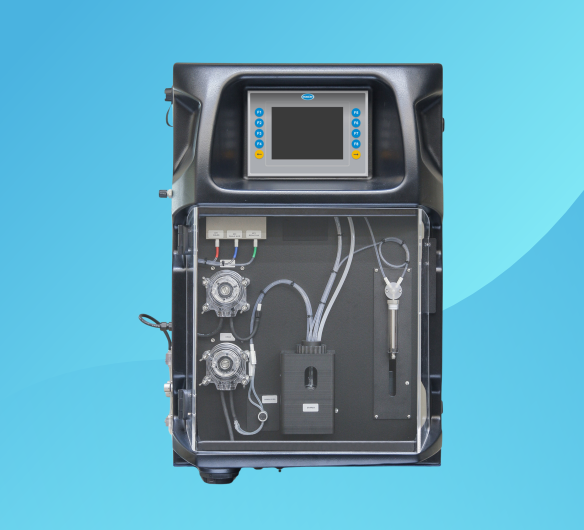

Applications: Influent for Wastewater, Primary Treatment, Secondary Treatment, drinking water, steam & power generation, surface water
These analyzers measure free (P-alkalinity) or Total Alkalinity, offering precise measurements of alkalinity in water samples. Guaranteed quick and accurate results
Discover MoreS1000 Portable Parallel Analyser (PPA)
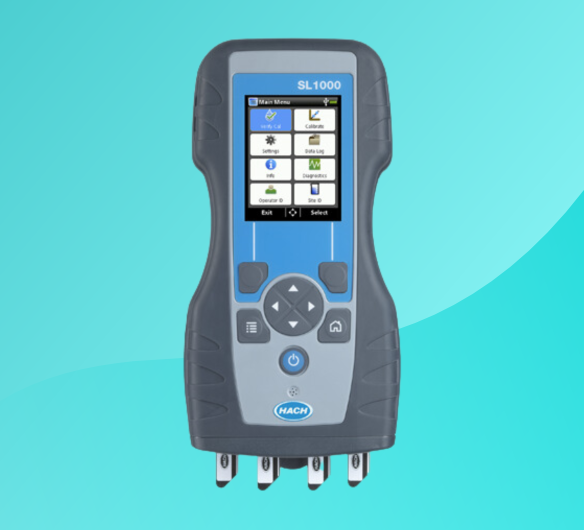

Applications: Boiler Water, Cooling Water. Groundwater, Membrane Protection, Municipal Water, Potable Water, QA/QC Lab, Source Water, Surface Water
With its ability to perform multiple tests simultaneously, the SL1000 streamlines alkalinity measurement alongside other parameters, offering on-the-go analysis for field applications like water quality assessments and environmental monitoring.
Discover MoreTitralab ® AT1000 & KF1000 Series
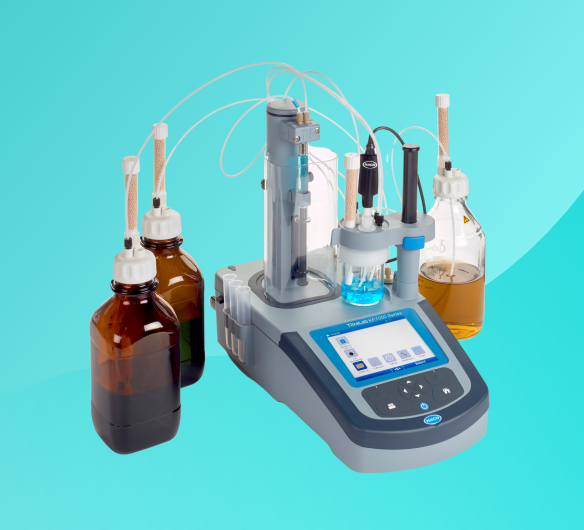

Applications: Influent for Wastewater, Primary Treatment, Secondary Treatment, Surface Water
Utilizing precise titration techniques, volumetric titration methods like those used in the AT1000 and KF1000 series ensure reliable measurement of alkalinity levels, crucial for maintaining optimal conditions in industrial processes and environmental monitoring.
Discover MoreSpectrophotometers
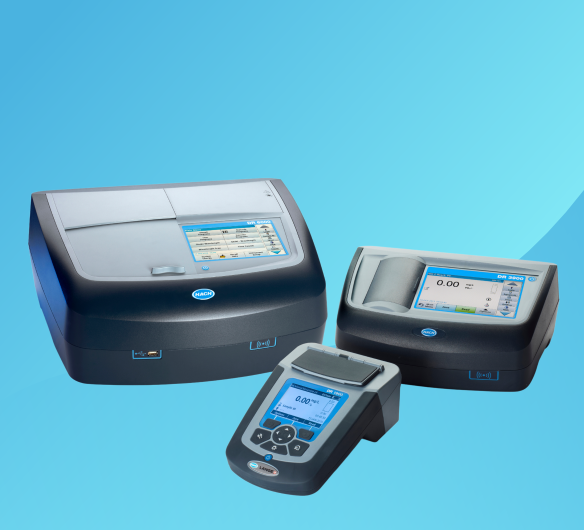

Applications: Groundwater, Influent for Wastewater, Municipal Water, Nutrient Monitoring, Primary Treatment, QA/QC Lab, Secondary Treatment, Surface Water, Membrane Protection, Pre-Treatment, Production Water, Potable Water
Hach has been innovating with spectrophotometry for over 70 years and offers many of the leading spectrophotometers in the water analysis market. These instruments enable the quantification of alkalinity through colorimetric methods, allowing for highly accurate and sensitive measurements essential in research, quality control, and regulatory compliance across industries.
Discover MoreTest Strips
With the simplicity and accuracy of Hach's alkalinity test kits, you can effortlessly ensure proper alkalinity levels in various field applications using drop count titration and color disc methods. Test strips are perfect for rapid on-site testing of alkalinity levels in water. Hach Total Alkalinity Test Strips provide a quick and easy way to estimate alkalinity levels in various water sources.
Discover MoreResources

Alkalinity in Drinking Water
Online measurement ensures drinking water quality by accurately monitoring the alkalinity, mitigating scaling or corrosion risks at Sydvatten Vomb drinking water treatment plant. Download our application note on cooling cycle analysis for further insights.
know More
Webinar
Back to Basics - Hardness and Alkalinity Management within Source Water Vulnerability
Watch Now
Which Processes Require pH Monitoring?
Wastewater Treatment
In wastewater treatment, alkalinity is an important parameter in determining the health and stability of various biological treatment processes. In anaerobic digestion, alkalinity and its ratio to the concentration of volatile fatty acids (VFAs) is the most important measurement for understanding the stability of this biological process. For optimal results, a digester should have a pH value between 6.5 and 7.5. However, just measuring the pH is not enough. In order to ensure sustainable and safe operation, the water must have a sufficient buffering capacity in order to compensate for changes in the acid concentration. A digester that is too acidic is toxic for the bacteria, especially for the methane-producing bacteria. Upsets due to the toxic conditions of low pH can be very costly due to reduced gas production, chemical addition for alkalinity, and significant increase in staff time and effort. Re-seeding an upset digester can take weeks and is very time consuming. In systems that are required to remove ammonia nitrogen, alkalinity is a key monitoring parameter for stable nitrification. Alkalinity values below 50 mg/L will inhibit the biological conversion of ammonia/ammonium to nitrite then to nitrate. Once alkalinity is depleted in a biological system, pH can begin to rapidly decline. When monitoring aerated biological nitrogen removal, pH is a commonly used and helpful indicator of system nitrification stability, but it is a lagging indicator. For maximum system stability monitoring, alkalinity monitoring is a good predictive measurement to indicate issues before they become critical.

Drinking Water Treatment
Alkalinity acts as a pH buffer in coagulation and lime-soda softening of water. Alkalinity is monitored throughout the water treatment process and in the distribution system to ensure the delivery of safe drinking water to the community. Knowing raw water alkalinity is very important for choosing the correct coagulants and setting up coagulation/flocculation process. With the correct knowledge of all critical parameters, coagulation process may be enhanced to remove total organic carbon (TOC) and reduce disinfection by-products (DBP) formation potential in the water prior to chlorination. Alkalinity of filtered water is often adjusted to control its corrosivity prior to release in the distribution system and measuring alkalinity of the tap water in the distribution network is important to ensure adequate corrosion control and avoid violation of the lead and copper rule (LCR).

Beverage Industry
Besides monitoring alkalinity in the feed water for boilers and cooling towers, this parameter is vital for evaluation of the source water used for production, because wrong or inconsistent alkalinity can adversely affect flavor and overall quality of beer, juices and other beverages.

Chemical Manufacturing for Industrial Processes
Along with other parameters, alkalinity is monitored during cooling processes to prevent corrosion to piping, condensers and dryers over time. Monitoring alkalinity, along with other key parameters during industrial wastewater treatment, helps facilities ensure compliance with chemical industry regulations, avoid permit violations, maximize efficiency, control cost, and operate at the highest possible levels of health and safety.

Processes Requiring Alkalinity Monitoring
Titration
Colorimetric Method
Alkalinity (Total) TNTplus Vial
Alkalinity TNTplus® chemistry and your Hach spectrophotometer are engineered to simplify water analysis for accurate results, everytime. For photometric determination of total alkalinity in drinking water, wastewater, and boiler water.
Contact Us
SL1000 Portable Parallel Analyzers (PPA)
The SL1000 performs multiple standard tests and make data management easy. SL1000 Portable Parallel Analyzer (PPA) performs the same tests with less than half the manual steps. Get highly accurate results, with less opportunity for errors, in a fraction of the time.
Contact UsTest Strips/Test Kits

Digital Titrator Test Kits
Hach digital titrators use a high-precision dispensation device and replaceable titrant cartridges for highly accurate results in the field or lab. More than 50 different paramaters and/or ranges are available to suit many testing applications.
Contact Us
Total Alkalinity Test Strips
Detects carbonates, bicarbonates, hydroxides, and salts. Ideal for drinking water, food processing, boilers, and aquatic biology. 50 tests per kit. Easy, disposable, and cost-effective for quick, quantitative results in the field or lab.
Contact Us
Alkalinity Test Kits
When it comes to ensuring the quality and safety of water, Hach's alkalinity test kits are indispensable. Designed to measure the presence of carbonates, bicarbonates, hydroxides, and other dissolved salts, these kits are crucial for food and beverage processors, boiler operators, and aquatic biologists. Our alkalinity kits contain 100 tests with a range of 10-4,000 mg/L. Shop alkalinity analyzers and alkalinity test kits for precise and reliable results.
Contact UsFrequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between hardness and alkalinity?
Hardness is the sum of the multivalent metal ions in solution, whereas alkalinity is a measure of the solution’s ability to neutralize acids (sum of hydroxide, carbonate and bicarbonate ions). In natural water systems, calcium carbonate is usually present and responsible for different characteristics of the water. Both hardness and alkalinity are expressed as a concentration of CaCO 3 for convenience of reporting a single number to represent multiple chemicals, and for ease in calculating a solution’s carbonate and non-carbonate hardness.
Understanding the distinction between Alkalinity and Hardness is vital for quality water analysis. Alkalinity plays a critical role in maintaining the balance of pH levels, acting as a shield against sudden shifts that could harm aquatic life. Conversely, Hardness measures the concentration of dissolved minerals, such as calcium and magnesium ions, which impact water quality and various industrial processes. Both Alkalinity and Hardness are essential aspects of water quality, forming the foundation of sustainable practices. The EZ5000 Series Alkalinity and Hardness Analyzers stands as a symbol of precision and efficiency in this field. Encased in an appealing, user-friendly design and governed by an integrated panel PC, these analyzers adapt seamlessly to diverse applications. They excel in measuring Hardness , navigating potential interferences like metal ions or suspended organic matter, and addressing Alkalinity concerns, such as electrode coating. Their rapid cycle time of 20-30 minutes ensures timely insights into water quality parameters, striking a balance between accuracy and efficiency. By integrating robust hardware with intelligent software features, the EZ5000 Series enables users to uphold optimal water quality standards, safeguarding ecosystems and supporting industrial processes effectively. In every analysis conducted, Alkalinity and Hardness emerge as pivotal factors, guiding the path towards a future where water remains a testament to human ingenuity and care.
What is the sample's alkalinity if the phenolphthalein indicator does not turn the sample pink?
Phenolphthalein alkalinity determination by titration uses a phenolphthalein indicator that changes from pink to colorless at the endpoint. If the sample does not turn pink after adding the indicator, the sample does not have phenolphthalein alkalinity. The sample will not have any phenolphthalein alkalinity if its pH is less than 8.3.
What are the interferences for Total Alkalinity, Colorimetric Method, TNTplus 870, Method 10239?
Samples with an acid capacity above 8 mmol/L must be diluted with deionized (DI) water that contains no carbon dioxide (CO 2). One can remove CO 2 from deionized water by boiling. The absence of CO 2 in the water used for dilution can be checked by carrying out a blank measurement. If the samples have high buffering capacity, dilute with DI water. CO 2 in the DI water will interfere when diluting samples or standards for this colorimetric test. The CO 2 free water is not as critical in the titration vs. the colorimetric procedure. The colorimetric test is more sensitive to slight changes in CO 2 concentration due to the colorimetric detection method and small sample volume used.
What are some common interferences in the alkalinity titration methods?
Some common interferences in alkalinity titration methods include:
- Chlorine – Chlorine at levels above 3.5 mg/L can cause a yellow-brown color when the Bromcresol Green-Methyl Red Powder Pillow is added. To remove the interference, pretreat the sample by adding 1 drop of Sodium Thiosulfate Standard Solution, 0.1 N per 100 mL sample, before adding any other reagents.
- Color or turbidity – Color or turbidity can make it difficult to see the color change at the endpoint. Do not filter or dilute samples with color or turbidity. Use a pH meter and titrate the samples to the specified endpoints:
Sample composition Phenolphthalein alkalinity Total alkalinity Alkalinity approximately 30 mg/L pH 8.3 pH 4.9 Alkalinity approximately 150 mg/L pH 8.3 pH 4.6 Alkalinity approximately 500 mg/L pH 8.3 pH 4.3 Contains silicates or phosphates pH 8.3 pH 4.5 Industrial wastes or complex systems pH 8.3 pH 4.5 Routine or automated analysis pH 8.3 pH 4.5 - Soaps, oily matter, suspended solids and precipitates – Oils or solids can collect on the pH probe and cause a slow response. Clean the probe immediately after use.
Can both alkalinity and hardness be measured together?
Yes, both alkalinity and hardness can be measured together using appropriate testing methods and equipment.
Download our application note on cooling cycle analysis to learn more about measuring alkalinity and hardness in water treatment processes.
DownloadWhat is the difference between Total Alkalinity vs. Phenolphthalein Alkalinity
Total Alkalinity
Total alkalinity is a measure in parts per million of all the alkali (all carbonate, bicarbonate and hydroxide ions) present in a sample. Therefore, total alkalinity is a measurement of water's ability to resist changes in pH.
Total alkalinity is determined by titration to a pH of 4.9, 4.6, 4.5, or 4.3, depending on the amount of carbon dioxide present.
Phenolphthalein Alkalinity
Phenolphthalein alkalinity (p-alkalinity) is determined by titration to a pH of 8.3 (the end point when phenolphthalein indicator changes color) and it registers the total hydroxide and one half the carbonate present. Phenolphthalein alkalinity is a subset of total alkalinity.
Typically, hard water is alkaline, while soft water is more acidic. However, exceptions exist in unusual circumstances.
What compounds contribute to alkalinity?
Alkalinity in water is primarily influenced by compounds like bicarbonates, carbonates, and hydroxides of calcium, magnesium, and sodium. These substances act as buffers against pH changes, ensuring water stability. Hach offers comprehensive solutions for accurately measuring and managing alkalinity levels, empowering industries to maintain water quality standards effectively




